⚙️ Configuring Rules
Welcome to the comprehensive guide for configuring Review Guardian! This document covers all available deterministic rules and their configuration options. These rules are fast, predictable, and perfect for enforcing clear-cut standards in your codebase.
Review Guardian uses a simple yet powerful YAML configuration file to define your team's code review standards. The .github/ship-guard.yml file follows a structured format that allows you to combine multiple rules, set severity levels, and target specific file paths.
📋 What You'll Learn
By the end of this guide, you'll understand:
- ✅ The structure of the
ship-guard.ymlconfiguration file - ✅ All available deterministic rules and their parameters
- ✅ How to use path filtering to target specific files
- ✅ Best practices for rule configuration
- ✅ Real-world examples for common scenarios
📁 Configuration File Structure
Every Review Guardian configuration follows this basic structure:
# .github/ship-guard.yml
version: 1 # Configuration schema version (required)
default_severity: 'error' # Default severity for rules (error/warning)
# Optional: Knowledge base for AI rules (covered in ai-reviews.md)
rag_sources:
- path: 'docs/architecture/**'
weight: 0.8
# Array of rules to enforce
rules:
- name: 'Rule description'
condition: 'rule-type'
severity: 'error' # Optional: overrides default_severity
paths: # Optional: target specific files
- 'src/**/*.ts'
excludePaths: # Optional: skip certain files
- '**/*.test.ts'
parameters: # Rule-specific configuration
# ... rule parameters
Configuration Properties
| Property | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
version | number | ✅ Yes | Configuration schema version (currently 1) |
default_severity | string | ❌ No | Default severity: "error" or "warning" |
rag_sources | array | ❌ No | Knowledge base paths for AI rules |
rules | array | ✅ Yes | List of rules to enforce |
🔧 Common Rule Properties
Every rule in Review Guardian shares these common configuration options:
Core Properties
| Property | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
name | string | ✅ Yes | Human-readable description of the rule |
condition | string | ✅ Yes | The rule type (see sections below) |
severity | string | ❌ No | Override default severity: "error" or "warning" |
Path Filtering
| Property | Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
paths | array | Only apply rule to these file patterns | ["src/**", "lib/**"] |
excludePaths | array | Skip these file patterns | ["test/**", "*.md"] |
Path Pattern Examples
rules:
- name: 'Critical files only'
condition: 'banned-terms'
parameters:
terms: ['console.log']
paths:
- 'src/components/**' # All files in components directory
- '*.js' # All JavaScript files in root
- 'lib/core.ts' # Specific file
excludePaths:
- 'src/components/dev/**' # Skip development components
- '**/*.test.js' # Skip all test files
💡 Pro Tip: Path filtering uses standard glob patterns. Order matters:
pathsfilter first, thenexcludePathsremove matches.
🛑 Deterministic Rule Reference
Banned Terms (condition: "banned-terms")
Prevents specific terms or patterns from appearing in your codebase. Perfect for catching debug code, deprecated APIs, or enforcing coding standards.
Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
terms | array[string] | ✅ Yes | — | List of banned terms |
caseSensitive | boolean | ❌ No | false | Whether to match case exactly |
useRegex | boolean | ❌ No | false | Treat terms as regex patterns |
ignoreComments | boolean | ❌ No | false | Ignore matches in comments |
Example
- name: 'No debug code in production'
condition: 'banned-terms'
severity: 'error'
paths:
- 'src/**/*.ts'
- 'lib/**/*.js'
excludePaths:
- '**/*.test.ts'
- 'scripts/**'
parameters:
terms:
- 'console.log'
- 'debugger'
- 'TODO'
- 'FIXME'
- 'HACK'
caseSensitive: false
useRegex: false
ignoreComments: false
Real-World Use Cases
- Debug Code: Prevent
console.log,debuggerstatements - Technical Debt: Block
TODO,FIXME,HACKcomments - Security: Prevent hardcoded passwords or API keys
- Deprecated APIs: Block usage of old function names
Require Changelog (condition: "require-changelog")
Ensures that user-facing changes are documented in your changelog file.
Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
changelogPaths | array[string] | ✅ Yes | — | Files to check for entries |
requireInPRDescription | boolean | ❌ No | false | Require changelog in PR description |
matchPattern | string | ❌ No | ".*\\bCHANGELOG\\b.*" | Regex to detect changelog entries |
minEntryLength | number | ❌ No | 10 | Minimum characters for valid entry |
Example
- name: 'Document user-facing changes'
condition: 'require-changelog'
severity: 'error'
excludePaths:
- 'docs/**'
- '*.md'
- 'test/**'
- '.github/**'
parameters:
changelogPaths:
- 'CHANGELOG.md'
- 'changelog/**/*.md'
requireInPRDescription: true
matchPattern: "^###?\\s+\\[?\\d+\\.\\d+"
minEntryLength: 20
Real-World Use Cases
- Release Management: Ensure all changes are documented
- Breaking Changes: Require explicit documentation of API changes
- User Communication: Track what users need to know about updates
Require Tests (condition: "require-tests")
Enforces that new code includes corresponding test files.
Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
testPaths | array[string] | ❌ No | ["**/tests/**", "**/*.spec.*", "**/*.test.*"] | Where tests usually live |
requireForPaths | array[string] | ❌ No | — | Which changed files must have tests |
matchStrategy | string | ❌ No | "co-located" | How to match tests to source files |
minChangedTests | number | ❌ No | 1 | Minimum test files changed |
Example
- name: 'New features must have tests'
condition: 'require-tests'
severity: 'warning'
paths:
- 'src/**'
parameters:
testPaths:
- 'tests/**'
- 'src/**/*.spec.ts'
- 'src/**/*.test.ts'
requireForPaths:
- 'src/**/*.ts'
matchStrategy: 'co-located' # expects tests near source files
minChangedTests: 1
Real-World Use Cases
- Test Coverage: Ensure new features are tested
- Quality Assurance: Prevent untested code from reaching production
- Regression Prevention: Maintain test coverage standards
Max File Additions (condition: "max-file-additions")
Prevents PRs from becoming too large by limiting the number of new files.
Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
maxFiles | number | ✅ Yes | Maximum number of new files allowed |
Example
- name: 'Keep PRs manageable'
condition: 'max-file-additions'
severity: 'warning'
excludePaths:
- 'docs/**'
- 'test/**'
- 'assets/**'
parameters:
maxFiles: 10
Real-World Use Cases
- PR Size Management: Encourage smaller, focused pull requests
- Review Efficiency: Make code reviews more manageable
- Change Tracking: Prevent overwhelming changes in single PRs
Security Scan (condition: "security-scan")
Performs basic security checks for common vulnerabilities and sensitive data exposure.
Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
checkSecrets | boolean | ❌ No | true | Scan for potential secrets |
checkVulnerabilities | boolean | ❌ No | true | Check for known vulnerable patterns |
customPatterns | array[string] | ❌ No | — | Additional regex patterns to check |
Example
- name: 'Security vulnerability check'
condition: 'security-scan'
severity: 'error'
parameters:
checkSecrets: true
checkVulnerabilities: true
customPatterns:
- 'AKIA[0-9A-Z]{16}' # AWS Access Key ID
- 'sk_live_[0-9a-zA-Z]{24}' # Stripe Live Secret Key
- "AIza[0-9A-Za-z\\-_]{35}" # Google API Key
Real-World Use Cases
- Secret Detection: Prevent hardcoded API keys and passwords
- Vulnerability Prevention: Block known dangerous patterns
- Compliance: Meet security audit requirements
File Size Limit (condition: "max-file-size")
Prevents individual files from becoming too large and hard to maintain.
Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
maxSizeKB | number | ✅ Yes | Maximum file size in kilobytes |
Example
- name: 'Keep files maintainable'
condition: 'max-file-size'
maxSizeKB: 500
severity: 'warning'
paths:
- 'src/**/*.js'
- 'src/**/*.ts'
excludePaths:
- 'src/generated/**'
- 'src/vendor/**'
Real-World Use Cases
- Code Maintainability: Prevent files from becoming too complex
- Performance: Keep files manageable for IDEs and tools
- Team Productivity: Encourage modular code structure
Line Length Check (condition: "max-line-length")
Enforces consistent line length limits for better code readability.
Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
maxLength | number | ✅ Yes | — | Maximum characters per line |
ignoreUrls | boolean | ❌ No | true | Skip lines containing URLs |
Example
- name: 'Maintain readable line lengths'
condition: 'max-line-length'
maxLength: 120
ignoreUrls: true
severity: 'warning'
paths:
- 'src/**'
excludePaths:
- '**/*.md'
- '**/*.json'
Real-World Use Cases
- Code Readability: Ensure consistent formatting
- Team Standards: Enforce coding style guidelines
- Tool Compatibility: Work well with various editors and displays
🎯 Complete Configuration Example
Here's a comprehensive example showing multiple rules working together:
# .github/ship-guard.yml
version: 1
default_severity: 'error'
rules:
# Code Quality
- name: 'No debug code in production'
condition: 'banned-terms'
severity: 'warning'
excludePaths:
- 'test/**'
- 'scripts/**'
- '**/*.test.*'
parameters:
terms:
- 'console.log'
- 'debugger'
- 'TODO'
- 'FIXME'
caseSensitive: false
# Documentation
- name: 'Document breaking changes'
condition: 'require-changelog'
severity: 'error'
excludePaths:
- 'docs/**'
- '*.md'
- 'test/**'
parameters:
changelogPaths:
- 'CHANGELOG.md'
requireInPRDescription: true
minEntryLength: 20
# Testing
- name: 'New features need tests'
condition: 'require-tests'
severity: 'warning'
paths:
- 'src/components/**'
- 'lib/**'
parameters:
testPaths:
- 'tests/**'
- 'src/**/*.spec.ts'
- 'src/**/*.test.ts'
matchStrategy: 'co-located'
minChangedTests: 1
# Security
- name: 'Security scan'
condition: 'security-scan'
severity: 'error'
parameters:
checkSecrets: true
checkVulnerabilities: true
customPatterns:
- 'AKIA[0-9A-Z]{16}'
- 'sk_live_[0-9a-zA-Z]{24}'
# Performance & Maintainability
- name: 'Keep files manageable'
condition: 'max-file-size'
maxSizeKB: 300
severity: 'warning'
paths:
- 'src/**'
excludePaths:
- 'src/generated/**'
- name: 'Maintain readable line lengths'
condition: 'max-line-length'
maxLength: 120
ignoreUrls: true
severity: 'warning'
paths:
- 'src/**'
excludePaths:
- '**/*.md'
# PR Management
- name: 'Keep PRs focused'
condition: 'max-file-additions'
severity: 'warning'
excludePaths:
- 'docs/**'
- 'test/**'
parameters:
maxFiles: 15
🏆 Best Practices
🎯 Start Small
Begin with 2-3 essential rules and gradually add more as your team adapts. Too many rules at once can overwhelm developers.
📁 Use Path Filtering Wisely
- Exclude test files from strict production rules
- Skip documentation from code quality checks
- Ignore generated code from manual review requirements
⚖️ Balance Severity Levels
- Use
"error"for critical issues that must be fixed - Use
"warning"for style preferences and suggestions - Start with warnings for new rules, then escalate to errors
🔄 Iterate Based on Feedback
- Monitor which rules cause friction
- Adjust severity levels based on team feedback
- Remove or modify rules that don't add value
🎨 Team-Specific Customization
- Frontend teams: Focus on component structure and testing
- Backend teams: Emphasize security and API documentation
- DevOps teams: Prioritize configuration and deployment files
📊 Rule Organization
Group related rules with comments for better maintainability:
rules:
# === CODE QUALITY ===
- name: 'No debug code'
# ...
# === SECURITY ===
- name: 'Security scan'
# ...
# === TESTING ===
- name: 'Require tests'
# ...
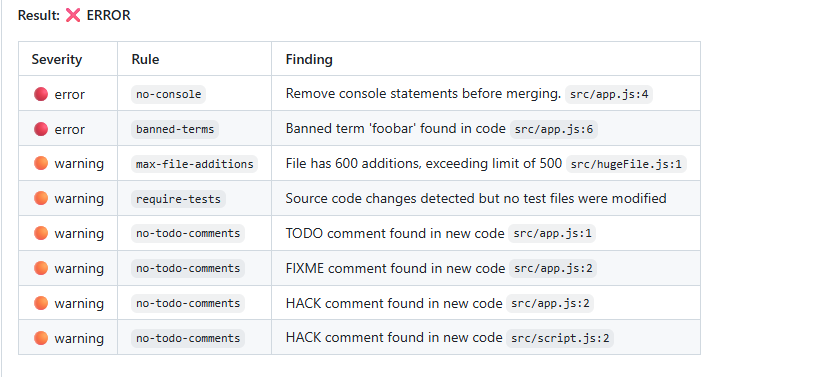
🚀 What's Next?
Now that you understand deterministic rules, you're ready to explore more advanced features:
| Next Step | Description | Link |
|---|---|---|
| 🤖 AI-Powered Reviews | Discover how to leverage AI for advanced code analysis and policy enforcement | ai-reviews.md |
| 📚 Advanced Configuration | Explore team-specific rules, RAG integration, and custom policies | advanced-configuration.md |
| 🔧 Troubleshooting | Common issues and solutions for rule configuration | troubleshooting.md |
Pro Tips for Success
- Test your rules on a small repository first
- Get team buy-in before enforcing strict rules
- Monitor rule effectiveness and adjust as needed
- Document your rules so team members understand the reasoning
Ready to take your code review process to the next level? Let's explore AI-powered reviews! 🚀